-

-
About Us
- Our Vision
-
Personalized Care
Personalized Care Personalized Care Intro
Diagnostic Tests
- Digital X-Ray
- DynaROM
- 3D Body Scanning
- Gastrointentinal Health
- Organic Acids
- Comprehensive Stool Analysis
- Food Sensitivity
- Dietary Antigen Complete
- Endocrinology
- Thyroid Panel
- DUTCH Hormone Test
- Neurotransmitter Profile
- Adrenal Profile
- Nutritional Status
- Vitamin D
- Homocysteine
- Methylmalonic Acid
- Urine Iodine
- Organic Acids
- Copper Zinc Profile
- Essential Fatty Acid Profile
- RBC Metals & Minerals
- Toxic & Essential Elements
- RBC Elements
- Urine Toxic Metals
- Hair Metals & Minerals
- Urine Halides
Treatments
- Avacen Therapy
- Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy (Anti-Aging)
- Chiropractic Care
- Electric Muscle & Nerve Stimulation
- Emsculpt Neo
- Emsella Treatment
- Erchonia Laser (Model EVRL)
- Exosomes
- Hair Restoration
- Headache & Migraine Treatment
- Hyaluronic Acid Injection
- Intersegmental Traction
- IV Nutrient Therapy
- Laser Lipo
- Massage Traction Chair
- PRP Facials
- PRP for Erectile Dysfunction
- PRP for Female Sexual Dysfunction
- PRP for Pain Relief
- PRP for Urinary Incontinence
- Semaglutide
- Shockwave Therapy for Cellulite & Skin Tightening
- Shockwave Therapy for Pain Relief
- Shockwave Therapy for Female Sexual Dysfunction
- Shockwave Therapy for Male Sexual Dysfunction
- Skin Rejuvenation
- Spinal Decompression
- TENS Unit
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
- Therapeutic Ultrasound
- Thyroid Care
- Trigger Point Therapy
- Durable Medical Equipment
- Ankle-foot Orthosis
- Cervical Rehab Coller
- Custom Foot Orthotics
- Lumbosacral Orthosis
- Osteoarthritis Knee Brace
- Wrist Brace
- FAQs
- Testimonials
- Pain Relief
- Weight Loss
-
Sexual Wellness
-
Anti-Aging
-
Resources
- Blog
- Video Library
- Store
-
Health Condition Library
Health Condition Library
- Ankle Osteoarthritis
- Bulging Spinal Disc
- Carpal Tunnel
- Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease
- Cervical Radiculopathy
- Elbow Bursitis
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Female Hormone Imbalance
- Female Sexual Dysfunction
- Fibromyalgia
- Foot Arthritis
- Frozen Shoulder
- Golfer’s Elbow
- Hand Arthritis
- Headache
- Hip Bursitis
- Hip Osteoarthritis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Knee Bursitis
- Knee Osteoarthritis
- Low Testosterone
- Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
- Migraines
- Musculoskeletal Pain
- Obesity
- Osteoarthritis
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Plantar Fibroma
- Rotator Cuff Injury
- Sciatica Pain
- Shoulder Bursitis
- Shoulder Osteoarthritis
- Tennis Elbow
- Thoracic Degenerative Disc Disease
- Urinary Incontinence
- Weight Gain
- Wrist Arthritis
- Wrist Bursitis
- Contact
Understanding Frozen Shoulder
Alternate Names: Frozen shoulder is commonly referred to as adhesive capsulitis. This name reflects the condition’s underlying cause, which involves the thickening and tightening of the shoulder joint capsule.
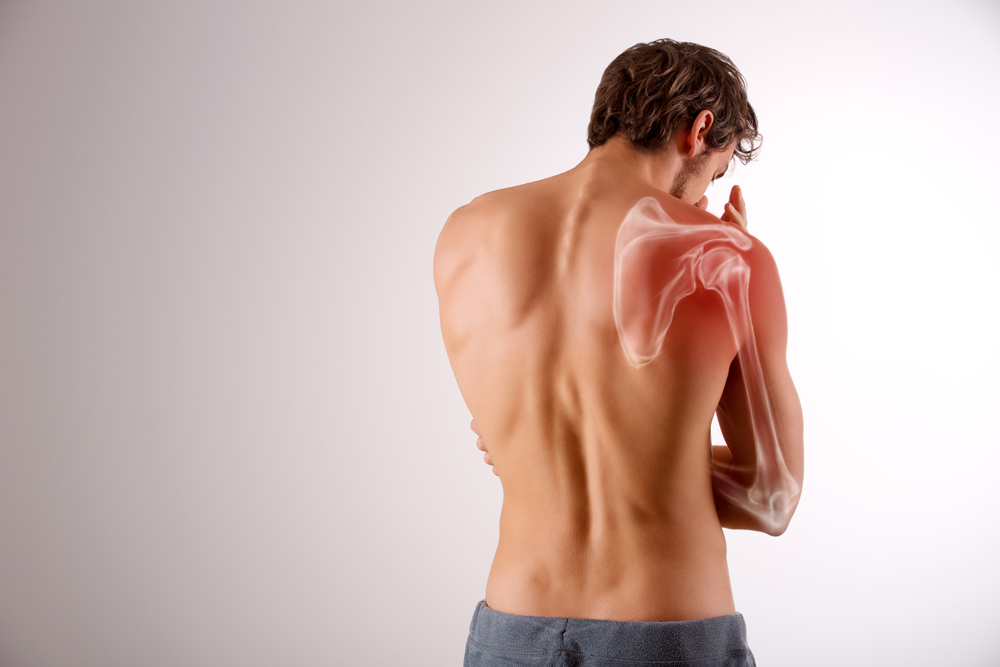
Introduction:
Frozen shoulder is a condition that affects the shoulder joint, causing pain and stiffness. It is characterized by the gradual loss of shoulder mobility, making it difficult to perform daily activities. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of frozen shoulder, including its alternate names, symptoms, causes, and multiple treatment options.
Symptoms:
The primary symptom of frozen shoulder is pain, accompanied by stiffness and limited range of motion in the affected shoulder. The condition typically progresses through three stages: freezing, frozen, and thawing. During the freezing stage, pain gradually intensifies, and shoulder movement becomes increasingly restricted. In the frozen stage, the pain may subside, but the shoulder remains stiff and immobile. Finally, during the thawing stage, the shoulder gradually regains its range of motion.
Causes:
The exact reason of frozen shoulder is not understood fully; however, certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition. These include age (most commonly affecting individuals between 40 and 60 years old), gender (more prevalent in women), certain medical conditions (such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, and cardiovascular disease), and previous shoulder injuries or surgeries.
Treatment Options:
Treating frozen shoulder involves a combination of non-surgical and surgical approaches, depending on the severity of the condition. Non-surgical treatment options include physical therapy, stretching exercises, pain management techniques (such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), and corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, where conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical interventions like shoulder manipulation or arthroscopic release may be considered.
Conclusion:
Frozen shoulder can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, causing pain and limiting shoulder mobility. However, with proper understanding and timely intervention, the symptoms can be managed effectively. This comprehensive guide has provided valuable insights into the alternate names, symptoms, causes, and multiple treatment options for frozen shoulder, empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their shoulder health.








