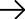-

-
About Us
- Our Vision
-
Personalized Care
Personalized Care Personalized Care Intro
Diagnostic Tests
- Digital X-Ray
- DynaROM
- 3D Body Scanning
- Gastrointentinal Health
- Organic Acids
- Comprehensive Stool Analysis
- Food Sensitivity
- Dietary Antigen Complete
- Endocrinology
- Thyroid Panel
- DUTCH Hormone Test
- Neurotransmitter Profile
- Adrenal Profile
- Nutritional Status
- Vitamin D
- Homocysteine
- Methylmalonic Acid
- Urine Iodine
- Organic Acids
- Copper Zinc Profile
- Essential Fatty Acid Profile
- RBC Metals & Minerals
- Toxic & Essential Elements
- RBC Elements
- Urine Toxic Metals
- Hair Metals & Minerals
- Urine Halides
Treatments
- Avacen Therapy
- Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy (Anti-Aging)
- Chiropractic Care
- Electric Muscle & Nerve Stimulation
- Emsculpt Neo
- Emsella Treatment
- Erchonia Laser (Model EVRL)
- Exosomes
- Hair Restoration
- Headache & Migraine Treatment
- Hyaluronic Acid Injection
- Intersegmental Traction
- IV Nutrient Therapy
- Laser Lipo
- Massage Traction Chair
- PRP Facials
- PRP for Erectile Dysfunction
- PRP for Female Sexual Dysfunction
- PRP for Pain Relief
- PRP for Urinary Incontinence
- Semaglutide
- Shockwave Therapy for Cellulite & Skin Tightening
- Shockwave Therapy for Pain Relief
- Shockwave Therapy for Female Sexual Dysfunction
- Shockwave Therapy for Male Sexual Dysfunction
- Skin Rejuvenation
- Spinal Decompression
- TENS Unit
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
- Therapeutic Ultrasound
- Thyroid Care
- Trigger Point Therapy
- Durable Medical Equipment
- Ankle-foot Orthosis
- Cervical Rehab Coller
- Custom Foot Orthotics
- Lumbosacral Orthosis
- Osteoarthritis Knee Brace
- Wrist Brace
- FAQs
- Testimonials
- Pain Relief
- Weight Loss
-
Sexual Wellness
-
Anti-Aging
-
Resources
- Blog
- Video Library
- Store
-
Health Condition Library
Health Condition Library
- Ankle Osteoarthritis
- Bulging Spinal Disc
- Carpal Tunnel
- Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease
- Cervical Radiculopathy
- Elbow Bursitis
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Fatigue
- Female Hormone Imbalance
- Female Sexual Dysfunction
- Fibromyalgia
- Foot Arthritis
- Frozen Shoulder
- Golfer’s Elbow
- Hand Arthritis
- Headache
- Hip Bursitis
- Hip Osteoarthritis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Knee Bursitis
- Knee Osteoarthritis
- Low Testosterone
- Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
- Migraines
- Musculoskeletal Pain
- Obesity
- Osteoarthritis
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Plantar Fibroma
- Rotator Cuff Injury
- Sciatica Pain
- Shoulder Bursitis
- Shoulder Osteoarthritis
- Tennis Elbow
- Thoracic Degenerative Disc Disease
- Urinary Incontinence
- Weight Gain
- Wrist Arthritis
- Wrist Bursitis
- Contact
Understanding Hip Osteoarthritis
Alternate Names: Hip osteoarthritis is also known as hip degeneration, hip joint arthritis, or simply hip arthritis.
Introduction:
Hip osteoarthritis, also referred to as degenerative joint disease of the hip, is a common condition that affects the hip joint. It is characterized by the gradual breakdown of the cartilage in the hip joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of hip osteoarthritis, including its alternate names, symptoms, causes, and multiple treatment options.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of hip osteoarthritis can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Hip pain: Individuals with hip osteoarthritis often experience pain in the hip joint, which may worsen with activity or prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
- Stiffness: The hip joint may feel stiff, especially after periods of inactivity or upon waking up in the morning.
- Reduced range of motion: As the condition progresses, the hip joint’s range of motion may become limited, making it difficult to perform certain movements.
- Swelling and tenderness: Inflammation of the hip joint can lead to swelling and tenderness in the affected area.
- Grating or clicking sensation: Some individuals may experience a grating or clicking sensation in the hip joint during movement.
Causes:
Hip osteoarthritis can be caused by various factors, including:
- Age: The risk of developing hip osteoarthritis increases with age, as the cartilage in the hip joint naturally wears down over time.
- Previous hip injuries: Individuals who have had previous hip injuries, such as fractures or dislocations, may be more prone to developing hip osteoarthritis.
- Genetics: Certain genetic factors can contribute to an increased risk of developing hip osteoarthritis.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional stress on the hip joint, increasing the likelihood of developing osteoarthritis.
- Repetitive stress: Activities that involve repetitive stress on the hip joint, such as running or heavy lifting, can contribute to the development of hip osteoarthritis.
Treatment Options:
There are several treatment options available for managing hip osteoarthritis, including:
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs or heat pads to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief.
- Rehab Therapy: Rehabilitation therapy for hip osteoarthritis aims to reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance quality of life. Physical therapy plays a crucial role, focusing on strengthening muscles around the hip joint, increasing flexibility, and improving joint mechanics. Therapists may employ exercises such as hip strengthening, stretching, and low-impact aerobic activities to alleviate symptoms and improve function. Modalities like heat, ice, or ultrasound may also be used to manage pain and inflammation. Additionally, education on joint protection techniques and lifestyle modifications can help individuals better manage their condition and maintain long-term hip health. Treatment plans are tailored to individual needs for optimal outcomes.
- Chiropractic Care: Chiropractic adjustments for hip osteoarthritis involve gentle manipulation techniques to improve joint function, alleviate pain, and enhance mobility. Chiropractors focus on realigning the hip joint and surrounding structures to reduce stress and improve biomechanics. Through targeted adjustments, they aim to restore proper alignment, reduce inflammation, and promote optimal function of the hip joint. Additionally, chiropractors may recommend exercises, stretches, and lifestyle modifications to complement adjustments and support long-term hip health. While chiropractic care cannot reverse osteoarthritis, it can help manage symptoms and improve overall hip function, providing relief and enhancing quality of life for individuals with hip osteoarthritis.
- Shockwave treatment: Shockwave therapy, or extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), is being explored as a treatment option for hip osteoarthritis. During the procedure, high-energy shockwaves are directed at the affected hip joint, stimulating tissue regeneration and reducing pain. Shockwave therapy aims to improve blood flow, decrease inflammation, and promote healing of damaged cartilage in the hip joint. While research on shockwave therapy for hip osteoarthritis is ongoing, preliminary studies suggest it may offer pain relief and improve function for some individuals.
- PRP therapy: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy is being investigated as a potential treatment for hip osteoarthritis. During PRP therapy, a concentrated solution of platelets and growth factors derived from the patient’s own blood is injected into the hip joint. This aims to stimulate tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain associated with osteoarthritis. PRP therapy may promote cartilage regeneration and slow down the progression of hip osteoarthritis. While research on PRP for hip osteoarthritis is ongoing, initial studies suggest it may provide pain relief and improve function, offering a promising minimally invasive option for managing symptoms and enhancing hip joint health.
Conclusion:
Hip osteoarthritis is a common condition and can negatively impact the quality of life. By understanding its alternate names, symptoms, causes, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and improve their hip joint health. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for a precise diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.